Schools are a cornerstone of every child’s development, shaping their academic, social, and psychological growth. However, for many students, it is also a source of significant stress, anxiety, and mental health challenges. This article delves deeply into how schools affect mental health, the factors that contribute to these issues, prevention strategies, and practical steps for parents and society to support children. We’ll also address common questions surrounding mental health in schools.Schools are a cornerstone of every child’s development, shaping their academic, social, and psychological growth. However, for many students, it is also a source of significant stress, anxiety, and mental health challenges.
This article delves deeply into how schools affect mental health, the factors that contribute to these issues, prevention strategies, and practical steps for parents and society to support children. We’ll also address common questions surrounding mental health in schools.
How Does School Affect Mental Health?
How Does School Affect Mental Health? The structure and demands of school can impact a child’s mental health in numerous ways. Academic pressure, bullying, fitting into social hierarchies, extracurricular demands, and the constant need to meet expectations often create an overwhelming environment for students.
In a school setting, mental health issues can range from mild stress to severe conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, or ADHD. While manageable stress can motivate students to achieve their goals, prolonged or unmanaged stress can significantly harm their emotional and mental well-being.
Studies indicate that nearly 1 in 5 children in schools suffer from some form of mental health issue, highlighting the urgency of addressing these concerns. Research has also linked excessive academic stress with diminished self-esteem, anxiety, and an increased likelihood of burnout later in life.
What Are the Most Common Mental Health Problems in Schools?
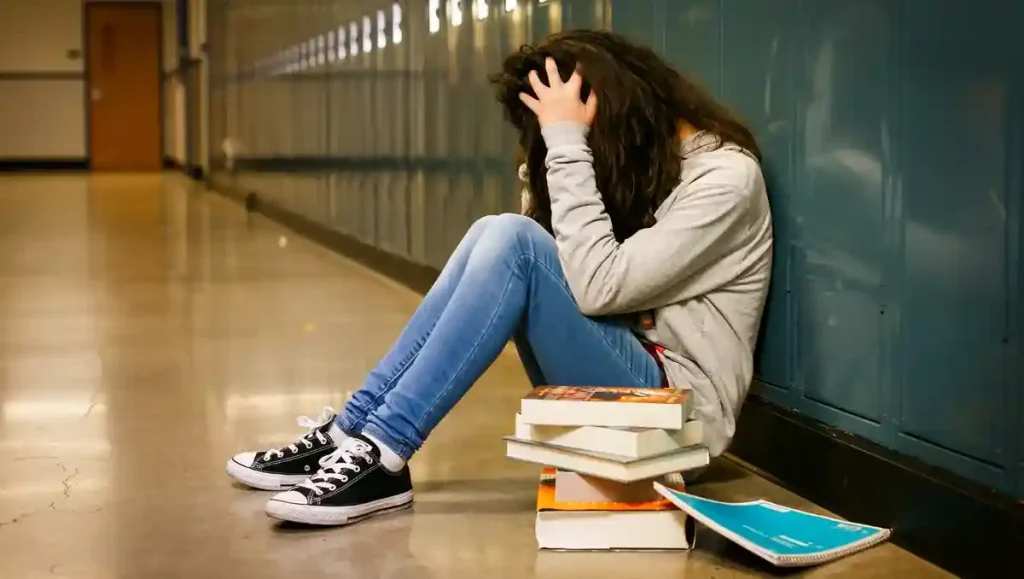

How Does School Affect Mental Health? The most common mental health problems affecting students in schools include:
- Anxiety Disorders: Generalized anxiety, test anxiety, and social anxiety are widespread among students who feel the pressure to excel academically or experience fear of social judgment.
- Depression: Characterized by persistent sadness, withdrawal, and a lack of interest in activities, depression is often linked to academic stress, bullying, or social isolation. Studies have found that approximately 15% of adolescents face some level of depression during their school years.
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): ADHD symptoms such as hyperactivity, inattention, and impulsivity can hinder a student’s performance in school and affect their relationships with peers.
- Bullying-Related Trauma: Victims of bullying often carry deep emotional scars, including feelings of worthlessness and, in severe cases, suicidal thoughts.
- Stress Disorders: The academic workload, coupled with parental and societal expectations, often causes chronic stress, with many students showing signs of burnout before they graduate.
What Is the Biggest Mental Health Problem for Students?
How Does School Affect Mental Health? For many students, anxiety disorders remain the most prevalent mental health condition. The constant pressure to perform well academically, fit in socially, and meet parental and societal expectations creates significant anxiety.
After the COVID-19 pandemic, these issues have worsened, with research showing that social isolation, gaps in education, and insecurity have caused an exponential rise in anxiety among students. A survey by the CDC reported a 25% increase in anxiety disorders among children between the ages of 12-17 during the post-pandemic years.
Anxiety can impact students in profound ways, affecting their ability to concentrate, complete tasks, and participate in class. This often creates a cycle of underperformance that further exacerbates their stress levels.
How Does School Cause Anxiety?

School can cause anxiety in several ways:
- Academic Pressure: High expectations to excel in tests, assignments, and overall performance create a performance-based mindset, amplifying fears of failure. Some studies show that over 50% of students feel “overwhelmed” by their academic workload.
- Social Dynamics: Peer pressure, the desire to fit in, and the fear of being judged can cause significant social anxiety in students. Social hierarchies in schools often leave many students feeling excluded or inadequate.
- Bullying: A study by the National Center for Educational Statistics revealed that about 20% of students experience bullying. This, combined with cyberbullying, can lead to long-term emotional trauma and mental health issues such as PTSD.
- Rigid Schedules: Schools often follow inflexible routines that prioritize academic achievement over students’ mental well-being, leaving limited space for relaxation, creativity, or addressing emotional concern
Why Am I So Scared of School?
For many children, fear of school (sometimes referred to as school phobia or school refusal) stems from a combination of factors, including:
- Fear of Failure: Academic pressure can lead to overwhelming self-doubt and persistent fears of underperformance.
- Fear of Embarrassment or Rejection: Situations like being called on in class, social rejection, or public humiliation terrify many students.
- Bullying: The dread of encountering bullies can make school feel unsafe or traumatic, leading some students to avoid attending altogether.
- Separation Anxiety: Younger children often struggle with being apart from parents or caregivers, creating additional stress around going to school.
These fears are deeply personal and valid. Understanding and addressing these concerns with empathy can go a long way in alleviating school-related anxiety.
What Is the 3-3-3 Rule for Anxiety?
The 3-3-3 rule for anxiety is a simple and effective grounding technique used to help manage sudden feelings of stress or panic. It works as follows:

- Look around and name three things you see.
- Focus on three sounds you hear.
- Move three parts of your body for example, your hands, legs, or neck.
This technique shifts focus away from intrusive thoughts, bringing the mind back to the present moment. While research specific to children is limited, mindfulness-based interventions like these have been shown to significantly reduce anxiety symptoms.
What Is the 54321 Method?
Another useful tool for managing anxiety is the 54321 method, which also helps bring calmness and focus through sensory grounding:
- 5: Identify five things you can see around you.
- 4: Recognize four things you can touch.
- 3: Name three things you can hear.
- 2: Notice two things you can smell.
- 1: Focus on one thing you can taste.
Teachers and parents can introduce this technique to children as a quick, on-the-spot stress management tool.
Is It ADHD or Anxiety?
ADHD and anxiety share overlapping symptoms, such as restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and feeling overwhelmed. Differentiating between the two requires careful observation. Here’s how they differ:
- ADHD: Symptoms include impulsivity, chronic distractibility, and hyperactivity. A child with ADHD may frequently interrupt others, lose focus in quiet settings, or thrive on high energy tasks.
- Anxiety: Focuses more on persistent fear or worry. A child with anxiety may avoid specific tasks or develop perfectionist tendencies due to fear of failure.
For instance, a child failing to submit homework may have ADHD due to difficulty focusing, or anxiety because they overthink every detail. A formal professional evaluation is often the best way to determine the root cause.
How Can Parents Ensure Their Child’s Safety and Well-Being?
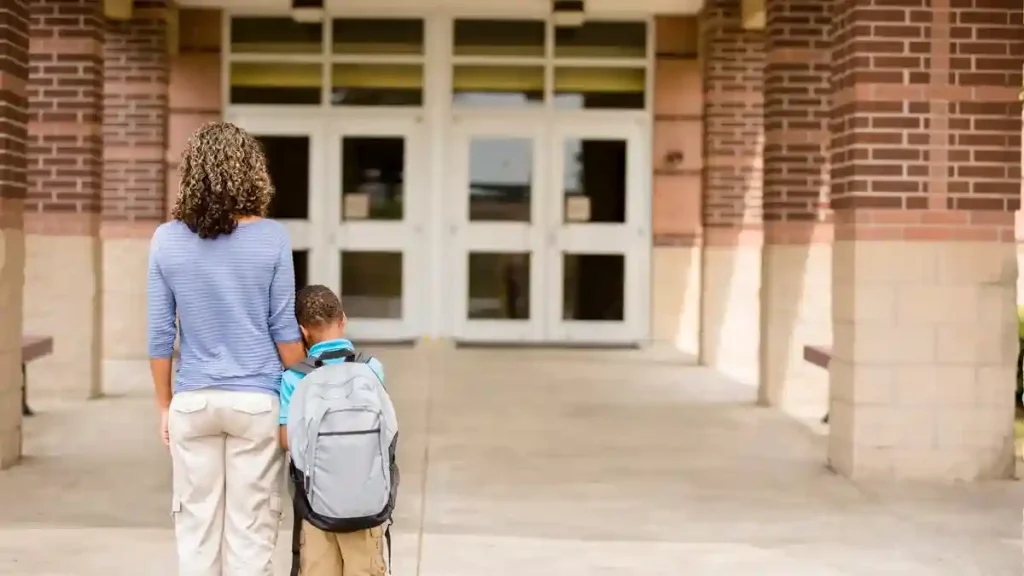

Parents play a vital role in safeguarding their child’s mental health. Here are some steps:
- Open Communication: Create a safe space for conversations about emotions. Asking non-judgmental questions like “How was your day?” builds trust.
- Recognize Warning Signs: Changes in mood, behavior, or consistent withdrawal are potential signs of distress.
- Avoid Excessive Pressure: Encourage effort and growth, emphasizing the joy of learning over grades.
- Teach Coping Skills: Introduce grounding exercises, mindfulness, or guided meditations.
- Seek Professional Help: When needed, involve school counselors, therapists, or child psychologists to provide targeted support.
What Role Does Society Play in Supporting Child Mental Health?
Society plays a critical role in promoting children’s mental health. Community involvement, inclusive school environments, and policies that reduce stigma can create an atmosphere conducive to better mental well being. Here’s how society can help:
- Reducing Stigma Around Mental Health: Normalizing conversations about mental health encourages students to seek help without shame.
- Integrating Mental Health Education in Schools: Teachers, parents, and students need awareness and training to identify early signs of mental health issues.
- Smaller Class Sizes and Accessible Resources: Reducing structural stress factors like oversized classrooms or inaccessible counselors can improve support for students.
- Advocating for Mental Health Policies: Advocating for policies like mandatory mental health breaks or funding for school psychologists ensures lasting systemic changes.
Reframing School as a Place of Growth and Compassion
Schools have the potential to shape not only a child’s academic success but also their lifelong mental well-being. By addressing issues like academic pressure, social hierarchies, and bullying, while incorporating tools such as mindfulness exercises and open communication, we can transform schools into nurturing spaces that prioritize mental health alongside education.
Ultimately, it takes a collective effort between parents, educators, policymakers, and students—to redefine what success looks like in schools. By fostering a culture of understanding and resilience, we can ensure that no child has to bear the weight of these challenges alone. Together, we can create a brighter and healthier future for every student.
Parents: Be the calm in their storm. Listen, nurture, and walk beside them because a healthy mind today builds a resilient heart for tomorrow.
Read more: Wake Up to Health: Men Health Awareness Month Starts Now 2025
Stay tuned for more guided help and follow us on Quora Page .




