What is DCS in Robotics, Distributed Control System (DCS) in robotics is a sophisticated automation framework that enables decentralized control of robotic processes. Unlike traditional centralized control systems, DCS allows multiple controllers to operate autonomously while communicating with each other. This structure enhances the efficiency, scalability, and reliability of robotic applications, making it a preferred choice in industrial automation, manufacturing, and process control.

In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, robotics plays a crucial role in automating tasks across various industries. From manufacturing to healthcare, robotics has become an integral part of modern industry. To ensure seamless operation, advanced control mechanisms are required. One such control mechanism is the Distributed Control System (DCS), which offers a structured approach to managing complex robotic systems. This article provides an in-depth exploration of DCS in robotics, including its architecture, advantages, applications, challenges, and future trends.
How DCS Works in Robotics
What is DCS in Robotics, A Distributed Control System (DCS) in robotics consists of multiple interconnected control units, each responsible for managing specific tasks within a larger robotic framework. This decentralized approach enhances system efficiency, autonomy, and scalability. By distributing control functions, DCS enables robotic systems to function with improved reliability, faster response times, and seamless adaptability. The working mechanism of DCS relies on several key components:

1. Control Units (Local Controllers)
Each robotic component, such as robotic arms, conveyor belts, and sensors, is equipped with a dedicated local controller. These controllers process real-time data, execute programmed tasks, and make independent decisions while remaining synchronized with other units. This modular approach ensures flexibility and minimizes downtime in case of faults.
2. Communication Network
A high-speed communication network links all controllers, facilitating real-time data exchange and task coordination. Industrial Ethernet, fieldbus protocols, and wireless communication technologies are commonly used to establish seamless connectivity. This network ensures efficient data transmission, enabling synchronized operations and quick decision-making across the system.
3. Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
The HMI serves as an interactive platform for operators to monitor system performance, troubleshoot issues, and control robotic functions. It provides a graphical interface displaying real-time data, alerts, and diagnostics. Through the HMI, operators can adjust parameters, optimize workflows, and intervene when necessary to maintain operational efficiency.
4. Supervisory Control System
Although local controllers function independently, a centralized supervisory control system oversees the overall robotic operation. This system ensures coordination among distributed controllers, optimizes resource allocation, and prevents conflicts between different robotic units. By analyzing system performance and implementing corrective measures, the supervisory system enhances operational stability and efficiency.
By integrating these components, DCS ensures a highly efficient, scalable, and intelligent robotic control system capable of adapting to dynamic industrial environments.
Advantages of DCS in Robotics
What is DCS in Robotics, Implementing a Distributed Control System (DCS) in robotics provides numerous benefits that enhance efficiency and reliability across industries. The key advantages include:

1. Scalability
DCS enables seamless integration of new robotic components without disrupting existing operations. This makes it ideal for expanding production lines and adapting to technological advancements. Industries can scale up automation processes efficiently without overhauling the entire system.
2. Flexibility
DCS allows customization and adaptation to diverse automation needs. It supports process optimization by enabling modifications to robotic workflows without major system disruptions. This flexibility helps industries meet evolving production demands efficiently.
3. Improved Efficiency
By distributing control tasks across multiple units, DCS minimizes bottlenecks and optimizes resource utilization. This results in faster, more precise robotic operations and reduces processing delays. Enhanced efficiency translates into higher productivity and better overall performance.
4. Real-time Control & Monitoring
DCS provides immediate responses to changing conditions, improving safety and reducing downtime. With real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance, potential system failures can be detected early, allowing preventive measures to be taken before issues escalate.
5. Redundancy and Fault Tolerance
One of the most significant advantages of DCS is its fault-tolerant nature. If a control unit fails, other functional units can compensate, ensuring continuous operation. This redundancy prevents complete system shutdowns, improving reliability and minimizing disruptions.
By incorporating these advantages, DCS strengthens robotic automation by making it more adaptable, resilient, and efficient in various industrial applications.
Comparison: DCS vs. Centralized Control Systems
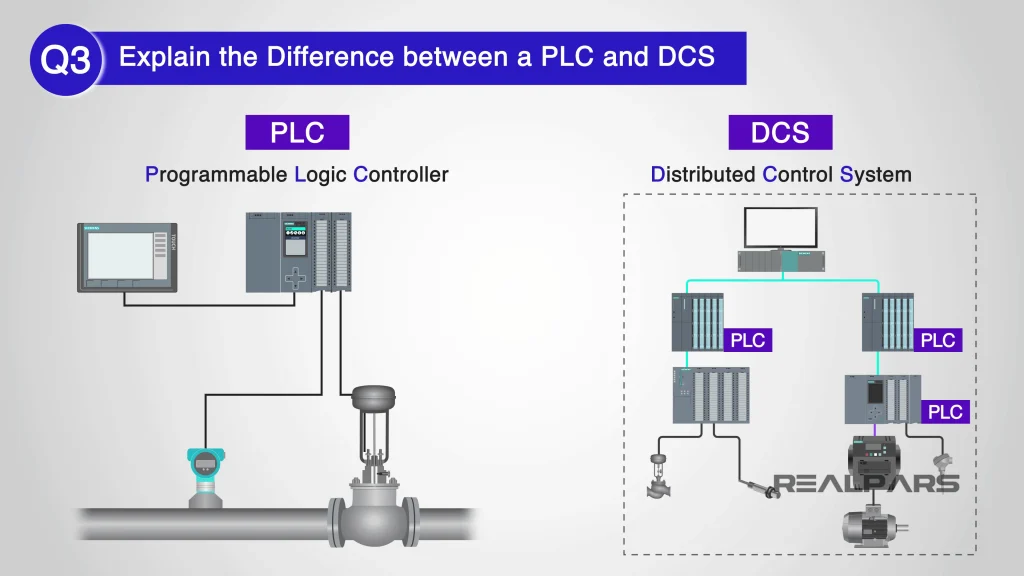
What is DCS in Robotics, A key distinction between DCS and centralized control lies in their architecture and operational efficiency:
| Feature | Distributed Control System (DCS) | Centralized Control System |
| Control Structure | Decentralized | Centralized |
| Reliability | High (redundancy reduces failure risk) | Lower (single point of failure) |
| Scalability | Easily expandable | Limited expansion |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable | Less adaptable |
| Response Time | Faster due to localized processing | Slower due to centralized data handling |
| Maintenance Complexity | Requires skilled personnel for maintenance | Easier to maintain due to single control unit |
| Implementation Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower cost but less flexible |
Applications of DCS in Robotics
What is DCS in Robotics, DCS (Distributed Control Systems) plays a crucial role in various robotic applications, enhancing automation, precision, and efficiency across multiple industries.
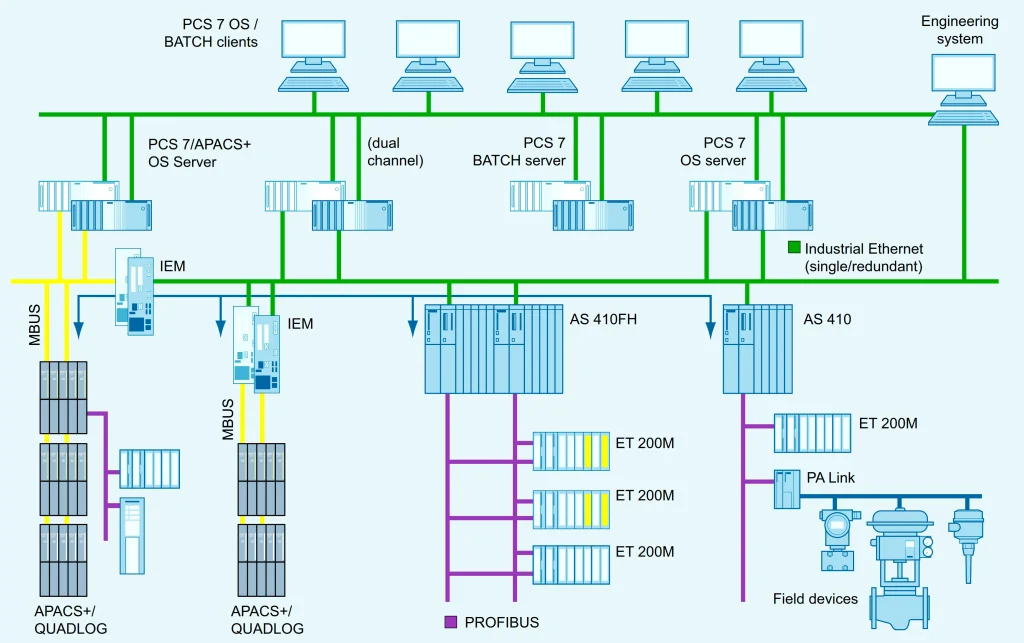
1. Manufacturing Automation
Factories utilize DCS to manage complex production lines where multiple robotic arms, conveyors, and automated machines work in coordination. By integrating DCS, manufacturers achieve high-speed production with minimal human intervention. Robotics in manufacturing ensures precision, consistency, and reduced operational errors, leading to improved product quality and efficiency.
2. Industrial Robotics
DCS is extensively used in industrial robotics to manage fleets of autonomous robots performing critical tasks such as material handling, welding, and assembly. Industries like automotive and electronics depend on DCS to maintain seamless production flow and optimize resource utilization. With real-time monitoring and adaptive control, DCS ensures enhanced productivity and reduced downtime in industrial environments.
3. Process Automation
Industries such as oil refining, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing rely on DCS to regulate robotic equipment with high precision. DCS enables automated control of complex processes, ensuring compliance with strict safety and regulatory standards. It also helps monitor environmental conditions and equipment performance, minimizing risks associated with hazardous operations.
4. Smart Warehousing
Warehouses and distribution centers increasingly employ autonomous robots powered by DCS to streamline inventory management. By reducing human intervention, DCS-driven robotics improves efficiency, optimizes storage, and enhances order fulfillment speed. With real-time tracking and intelligent scheduling, warehouse automation significantly reduces errors and operational costs.
5. Healthcare and Medical Robotics
DCS is revolutionizing healthcare robotics by enabling precise control of surgical robots, diagnostic machines, and automated drug dispensing systems. The healthcare industry benefits from DCS in enhancing surgical accuracy, improving patient safety, and ensuring consistent medical procedures. Robotic-assisted surgeries and automated laboratory processes driven by DCS are paving the way for advanced medical innovations.
In conclusion, DCS in robotics offers unparalleled efficiency, safety, and accuracy across industries, making it an essential technology for modern automation.
Challenges and Future Trends What is DCS in Robotics
Challenges
- Complex Integration: Implementing DCS requires sophisticated network architecture and skilled personnel.
- High Initial Cost: Advanced hardware and software investments can be costly.
- Security Risks: As DCS relies on network communication, cybersecurity measures must be robust to prevent breaches.
- Data Synchronization Issues: Ensuring real-time data consistency across distributed controllers is challenging.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting Complexity: Decentralized control systems require specialized knowledge for troubleshooting and maintenance.
Future Trends
- AI-Driven DCS: Machine learning and artificial intelligence will enhance predictive maintenance and process optimization. AI-powered control systems will enable self-learning capabilities, further improving system efficiency.
- Edge Computing Integration: Combining DCS with edge computing will enable faster and more localized data processing, reducing reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure.
- 5G Connectivity: Faster, low-latency communication will improve real-time control and monitoring in distributed systems. 5G networks will enhance the efficiency of industrial automation by supporting seamless device communication.
- Blockchain for Security: Implementing blockchain technology in DCS can enhance security by ensuring tamper-proof data exchanges.
- Robotics as a Service (RaaS): Cloud-based DCS models will enable businesses to access robotic automation as a service, reducing upfront investment costs.
Here are five FAQs based on the article on DCS in Robotics, along with their answers:
FAQs on What is DCS in Robotics
- What is a Distributed Control System (DCS) in robotics?
A Distributed Control System (DCS) in robotics is an automation framework that decentralizes control functions across multiple controllers. These controllers operate independently while communicating with each other, enhancing efficiency, reliability, and scalability in robotic applications. - How does DCS improve robotic automation?
DCS optimizes robotic automation by distributing tasks among multiple control units. This approach minimizes bottlenecks, ensures real-time control, increases fault tolerance, and enhances overall system efficiency. It also allows for seamless scalability and adaptability to changing industrial needs. - What are the key components of a DCS in robotics?
The main components of a DCS in robotics include:- Control Units (Local Controllers): Manage specific robotic functions independently.
- Communication Network: Enables real-time data exchange between controllers.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Allows operators to monitor and control robotic functions.
- Supervisory Control System: Oversees and optimizes overall robotic operations.
- What industries benefit from DCS in robotics?
Several industries leverage DCS in robotics, including:- Manufacturing automation (assembly lines, robotic arms).
- Industrial robotics (welding, material handling).
- Process automation (oil refining, pharmaceuticals).
- Smart warehousing (inventory management, order fulfillment).
- Healthcare (robotic surgeries, automated diagnostics).
- What are the future trends in DCS for robotics?
Emerging trends in DCS for robotics include:- AI-powered predictive maintenance for improved efficiency.
- Edge computing for faster local data processing.
- 5G connectivity for real-time communication.
- Blockchain integration for enhanced cybersecurity.
- Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) for cost-effective automation solutions.
Conclusion What is DCS in Robotics
What is DCS in Robotics, DCS in robotics is revolutionizing industrial automation by providing a scalable, flexible, and efficient control framework. By decentralizing operations, it enhances system reliability, real-time monitoring, and adaptability. The growing integration of AI, edge computing, and 5G technology will further propel the evolution of DCS in robotics, making it a cornerstone of future automation. Industries that embrace DCS will benefit from increased productivity, reduced downtime, and enhanced operational efficiency, positioning themselves for long-term success in an increasingly automated world.
Read more: Explore Nexus Globes for the latest news on tech, health, and entertainment.
What Purpose Do Fairness Measures Serve in AI Product Development?